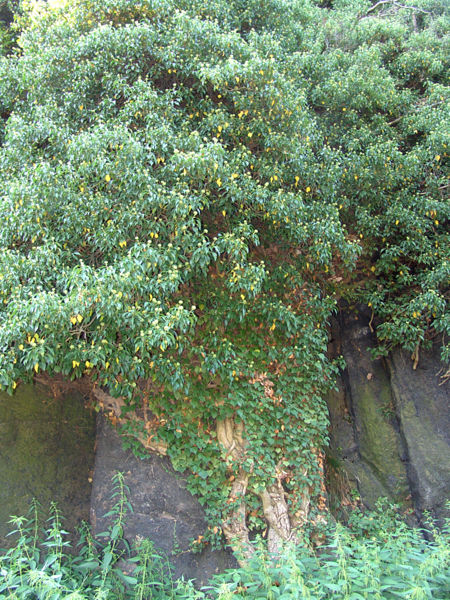
“The wren, the wren, the king of all birds, St. Stephen’s Day was killed in the furze; Although he be little his honour is great, so, good people, give us a treat.” – Peter Ellis (the Druids)[i]
The Roots:
The seventeenth letter of the Ogham is Ohn, which is usually listed as the Gorse. According to Robert Graves, some lists use Scotch Broom instead[ii].
Gorse is also known as Sea Gorse, Furz, Furze, Furse or Whin. It is a close relative to the Broom plant belonging to the same tribe Genisteae, with the main differing quality being its sharp thorns or spikes. In Cad Goddeu –the Battle of the Trees- Broom even seems to become the parent of the Gorse -within the poem- when the story says that, “The Brooms with their offspring [arrived?]: the Furz was not well behaved, until he was tamed…” Interestingly, though unrelated, the “Gorse” is also said to be great in battle elsewhere in the same poem[iii].
James Frazer, in the Golden Bough, says that in folk rituals the Furz and the Broom were often interchangeable. This may be why some of the Ogham lists use Broom instead of Gorse. It may also be why Robert Graves left Broom out of his Ogham list as the plant for Ngetal[iv] and instead replaced it with the Reed Grass. Perhaps he thought that the Broom and Gorse were too similar to one another to each have a letter in the Ogham? Another possibility that I have mentioned before is that he may have chosen this placement more to support his tree calendar theory than for any other historical or mythological significance.
Liz and Colin Murray in the Celtic Tree Oracle said that Gorse represented the collecting together of various objects for ones journey. They compared the Gorse to the magpie, which is a highly intelligent bird believed to collect shiny objects for its nest.
John Michael Greer agrees saying that Ohn is the few of attracting, of combination, possibility, growth and potential[v].
Nigel Pennick also believes similarly that Ohn is the letter of continuous fertility, collecting and dispersal[vi].
Robert Graves reminds us that Furz is one of the very first flowers to be visited by bees collecting nectar and pollen in the spring. It is a plant, he claims, that is also good to use against witches[vii].
Eryn Rowan Laurie says that Gorse is the plant for foundations and the journey. Ohn is also related to ones path, choices, direction and intention. The energy of the Broom plant, on the other hand, is of healing and of wounding[viii].
The Broom is listed in the Ogham tract as associated to healing and physicians. The Gorse is associated to the wheel of the chariot, and by extension to travelling[ix].
Both the Broom and the Gorse have strong connections to witches and to the fairies. The Gorse in particular has a connection with the Cailleach, the great hag Goddess who is sometimes named the Queen of the Fairies.
Ohn is the few of journeys and of the preparation for the mission at hand. The Gorse speaks of darker tools and attitudes needed to succeed upon the path, while the Broom reminds us that we must be ready to heal and create if we are called upon to do so.
The Trunk:
According to James Frazer in the Golden Bough, “old straw, furz or broom was burned in Scotland for Beltane fires “a little after sunset.” Broom was also burned to repel witches.
The connection of Gorse, or Furz, and Broom to witches, fairies and protection seems to radiate throughout many myths. It is never entirely clear however if the plants are beneficial or harmful. Perhaps they are both.
The Golden Bough tells us that Gorse was burned as a sort of smudge to bless and protect the cattle from witches on the Isle of Mann.
In the Fairy Faith in Celtic Countries by W.Y. Evans-Wentz, 1911, we are told that Furz fires were sometimes built as a gift to the fairies to keep them warm. The book also says that any gifts of gold given to a person by the fairy may turn to Furz blossoms if that person told another of the source of their newfound wealth.That was if their telling didn’t outright kill them! Eryn Rowan Laurie also speaks of the gold found beneath the Gorse.
The same text gives us a story from the Isle of Mann. There was apparently a “strange woman” who was seen to have materialized within the Gorse bush and walked over it, “where no person could walk”, and touched one of the cows that belonged to the witness. A few days later the heifer fell over dead. Witches and fairies seemed to have always been after the cows in those days, as well as the milk and butter that they produced, as this was the wealth of the Celtic ancestors. It seems to have been a common belief that witches and fairies coveted this wealth.
In the Fairy legends of the South of Ireland by Thomas Crofton Croker, 1825, we are also told of an apparition that growled like “burning Gorse.”
The Broom plant seems to be a little lighter.
The most famous story involving Broom was previously covered when we discussed Duir, the Oak, and that is the story of Blodeuwedd, “flower face.” She was created by Gwydion and Math to be the wife of Lleu who had a curse placed on him, by his mother, to wed no mortal woman. This story is found in the Mabinogion. The plants used to create Blodeuwedd are listed as the flowers of Oak, meadowsweet and Broom. She was created from vegetation and was thus not mortal and a suitable wife for Lleu. In this highly symbolic and charged tale Blodeuwedd ends up betraying Lleu with Gronw Pebyr, a passing hunter. Gronw is eventually killed and Blodeuwedd is made into the owl, a bird which is hated by all, by Gwydion to punish her.
(E. Wallcousins. From Celtic Myth and Legend. Charles Squire, 1905)
While the Broom’s most famous story is one of creating a beautiful woman the Gorse’s most relevant tale seems to speak of old age, death and destruction.
A most interesting story is told of the Cailleach in the Carmina Gadelica that relates to the Gorse. The Cailleach, the great hag, is often seen as the goddess of winter. In the first week of April she would use her magic wand to keep the vegetation from growing by swinging it back and forth over the struggling signs of new growth. Eventually, she would be overpowered by the elements of spring. She would eventually admit defeat and fly off in a rage screaming:
“It escaped me below, it escaped me above,
It escaped me between my two hands,
It escaped me before, it escaped me behind,
It escaped me between my two eyes,
It escaped me down, it escaped me up,
It escaped me between my two ears,
It escaped me thither, it escaped me hither,
It escaped me between my two feet.
I throw my druidic evil wand
Into the base of a withered hard Whin bush,
Where shall not grow ‘fionn’ nor ‘fionnidh,’
But fragments of grassy froinnidh.”
This chant extracted from Visions of the Cailleach by Sorita d’Este and David Rankine gives the reason why other plants do not grow beneath the Gorse[x]. It is also a clue as to the harnessing of the powers of winter, to witches to come, through the use of a wand of Gorse.
Whether the Gorse or Broom is seen as either positive or negative, it is clear that these plants are flora of a once highly respected magical tradition.
The Broom seems to offer wealth, healing, and manifestation.
The Gorse or Furz seems to offer wealth, destruction, and protection from manifestation.
Both plants could have been seen as powerful allies, upon the road that one was to journey upon.
The Foliage:
When one considers that the Gorse and the Broom both grew, and continue to grow, out in the open and needed to be tamed -by our ancestors- then the parallels between the two plants becomes apparent. Both plants were often burnt back by shepherds and farmers to preserve the land from being overwhelmed. Gorse on the one hand had spiky thorns while the Broom was softer but just as prolific.
In the Ogham Tract[xi] the trees and plants of the Ogham are listed according to their rank. Some trees are seen as chieftain trees, some are seen as peasant trees and some are seen as shrub trees. Interestingly enough, the Furz is listed as a chieftain tree but -as Whin- is listed again as a peasant tree[xii]. It is also assumed that Broom is listed as a shrub tree in this particular order by its absence. Under Brehon law[xiii], however, both the Broom and the Furz are given the lowest rank of “bramble” trees.
The listing of Gorse as a chieftain plant during these earlier times probably had a great deal to do with the respect that was given to it. There seems to be a common theme in the tree and plant mythology of the Celtic ancestors and that was that the thorn plants –Hawthorn, Blackthorn, and Blackberry- were protected by the fairies and thus were sacred, feared, or both.
According to Eryn Rowan Laurie the Gorse was used in some parts of Ireland instead of the Hawthorn as the May bush. This could have only been possible if the Gorse was a greatly respected plant of the times, for it to have been used in this way.
Unrecognized and powerful, like the ivy plant, the Gorse and Broom are considered in many places to be invasive and aggressive plants that threaten the native growth of local flora. Today these weeds have sought out the attention of millions of dollars in a bid to remain acknowledged and recognized.
Perhaps, this is merely a coincidence.
“Our outer world is progressively diminished and corrupted by abuse of technology, greed and indifference to the welfare of other orders of life, and romantic adventurers often complain that there is nothing left to explore, no liberating challenge or experience. But liberation comes from within, both within ourselves and within the Underworld that is the original source and image for our planet.” –R.J. Stewart(Earth Light, 1992)

[i] Another version of this old Irish song is found in the Golden Bough by James Frazer.
[ii] The White Goddess.
[iii] D.W. Nash translation. Ibid.
[iv] Ngetal is the thirteenth letter of the Ogham.
[v] The Druid Magic Handbook.
[vi] Magical Alphabets.
[vii] The White Goddess.
[viii] Ogam: Weaving Word Wisdom.
[ix] http://www.maryjones.us/ctexts/ogham.html
[x] A similar tale found in the same book has the Cailleach throwing a black hammer instead of a wand, and having it land beneath the Holly tree instead of the Gorse. Again, this is the reason given for the scant vegetation found beneath the Holly.
[xi] http://www.maryjones.us/ctexts/ogham.html
[xii] Robert Graves believed that this was a mistake and should have been Holly instead.
[xiii] Irish law. The White Goddess.