“Better the bramble than the black-thorn, better the black-thorn than the devil. He who would go in the bramble for me, I would go in the thorn for him” – Proverb (Alexander
Carmichael: Carmina Gadelica Vol. II. 1900)
The Roots:
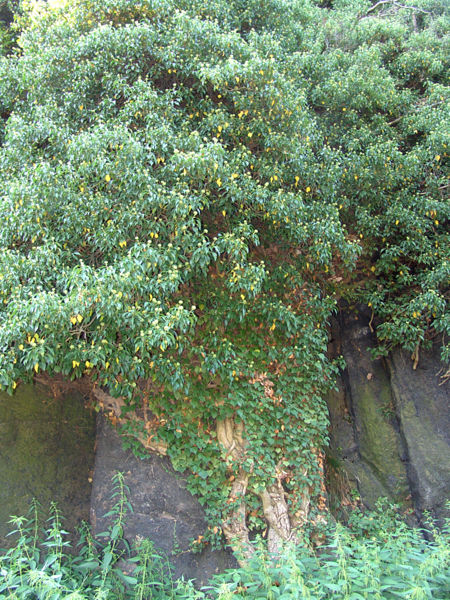
The fourteenth letter Straif is the few of the blackthorn, which is also known as the sloe tree.
Blackthorn is often associated with misfortune and tragedy, but it can also be seen as a tree of great power. Robert Graves said that the blackthorn was “unbeloved by men”, claiming that it was both unlucky and that it was associated with black magic[i].
Liz and Colin Murray further claimed that this letter was a harbinger of necessary change and that it was a warning of a coming season of discontent[ii]. John Michael Greer –in more recent times- has a very similar meaning listed in the Druid Magic Handbook saying that Straif is the letter of difficult change. Greer says that there is no choice but to move forward during such trying circumstances.
What may be seen as great change by some, can also be viewed as mighty power by others.
Nigel Pennick calls the blackthorn, “a major tree of magical power”. He claims that the influences of the blackthorn reaches into both worlds[iii].
Eryn Rowan Laurie says that Straif is the few of spiritual work, secrets, shapeshifting, divination and change[iv].
The blackthorn is a tree -or thorn bush- of the Sidhe. Straif is connected to the Leanan-Sidhe and by association to the goddess Aine and the Ban-Sidhe. It is considered sacred to the fairies and was believed to be very unlucky to cut or harm the tree at certain times of the year, most especially May 11th and November 11th.
Straif, the blackthorn, is the tree of ill omens, transformation and power.
The Trunk:
In the Fairy Faith in Celtic Countries (1902) W.Y. Evan Wentz lists the Lunantishee as tribes of fairy that were responsible for guarding the blackthorn or sloe trees. Sidhe is pronounced shee, so despite the confusing variations in spelling -and the lack of
recurrence of the above spelling in the old books- Wentz was speaking of the Leanan Sidhe.
The Leanan Sidhe is called the, “Spirit of Life” by Lady Wilde in Ancient Legends, Mystic Charms and Superstitions of Ireland (1911). She then calls the Ban Sidhe (Banshee)
the, “Spirit of Death”. The Leanan Sidhe would give inspiration to the musician or poet and would sometimes give men valour or strength in battle. The Ban Sidhe on the other hand, would foretell doom. The Sidhe –sometimes the Tuatha De Danaan- have very blurred lines in the Irish Celtic legends with the gods of the ancestors.
Interestingly enough, it was believed that the blackthorn was sacred to the goddess because of the contrast of the trees colors during various seasons. The white flower of spring symbolizes the beautiful, peaceful and life-giving aspect of the goddess while the black fruit of autumn symbolize the death dealing destroyer-of-life personae of the same goddess. The tree balances white and dark, but also has a red sap that can be seen as the third colour sacred to goddesses of the land[v].
It is likely that the blackthorn was a revered and respected tree associated with the Sidhe before the coming of Christianity and later became feared to greater degrees. The new faith brought the idea that spirits that did not exist in the Hebrew texts, were just as likely to be aspects of the devil or wandering demons seeking out the souls of non believers[vi].
It should be no surprise then that the Leanan Sidhe is sometimes seen as a vampire-like figure that makes men fall in love with her to steal their souls. The solitary version of the Leanan-Sidhe is also often seen as being Aine the goddess who is sometimes referred to as the Fairy Queen[vii].
The following story is taken from Gods and Fighting Men by Lady Gregory (1904) and is found in Part I: Book IV: Aine. It sheds some light on the contrast of beauty and darkness that makes up this aspect of the Leanan Sidhe:
AND as to Aine, that some said was a daughter of Manannan, but some said was the Morrigu herself, there was a stone belonging to her that was called Cathair Aine. And if any one would sit on that stone he would be in danger of losing his wits, and any one that would sit on it three times would lose them for ever. And people whose wits were astray would make their way to it, and mad dogs would come from all parts of the country, and would flock around it, and then they would go into the sea to Aine’s place there. But those that did cures by herbs said she had power over the whole body; and she used to give gifts of poetry and of music, and she often gave her love to men, and they
called her the Leanan Sidhe, the Sweetheart of the Sidhe.
And it was no safe thing to offend Aine, for she was very revengeful. Oilioll Oluim, a king of Ireland, killed her brother one time, and it is what she did, she made a great yew-tree by enchantment beside the river Maigh in Luimnech, and she put a little man in it, playing sweet music on a harp. And Oilioli’s son was passing the river with his step-brother, and they saw the tree and heard the sweet music from it. And first they quarrelled as to which of them would have the little harper, and then they quarrelled about the tree, and they asked a judgment from Ollioll, and he gave it for his own son. And it was the bad feeling about that judgment that led to the battle of Magh Mucruimhe, and Oilioll and his seven sons were killed there, and so Aine got her revenge.
(Merlin and the Fairy Queen. John Duncan. sacred-texts.com)
The association of the powerful Leanan Sidhe, the Fairy Queen Aine, and likely the Ban Sidhe, to the blackthorn warns us that this is no tree to be trifled with. Its strong ties to the fairy kingdom are reminiscent of the powers of the hawthorn.
The blackthorn is, in fact, often considered to be a sister tree to the hawthorn. It can have very negative qualities, however, as it was a tree that was used – most especially the thorn- in black magic. It was believed that during the time of the witch hunts -the purging of the older pagan beliefs- that it was the devil himself that would prick the witch’s finger with a thorn as a sort of initiation. Thus the superstition of the blackthorn became further compounded over time through fear and persecution[viii].
Straif, the blackthorn, has protective qualities as well. Besides being used in hedging it was also thought to provide protection against ghosts, those restless spirits, that were found throughout Ireland[ix].
The tree of fairies and witches, the blackthorn not only exists in both worlds simultaneously, it exists –it can be argued- more in the Otherworld than it does on the land before us. The tree can protect us, but it can also harm us if we are not careful and respectful. Straif, the fourteenth few, is the tree of magical power and
transformation.
The Foliage:
The Blackthorn does not grow in Western North America but has naturalized in parts of Eastern North America[x].
Blackthorn, or prunus spinosa, is part of a family of 200 species. The blackthorn is related to the plum, apricot, almond, peach and cherry trees. Thus, the blackthorn’s closest relatives in the Pacific Northwest are the cherry trees. The similarity is apparent, if and when the sloe become a tree.
This is one of the problems that Eryn Rowan Laurie warned us about. When the tree of the “Ogham Tree Calendar” does not exist in a certain region what does one replace it with when the need for working with that plant directly surfaces?
In its tree form the similarity to cherry trees is apparent. The cherry trees do not seem to ever become the thorny shrubs that are more common for the blackthorn though. What tree would replace it in its absence then? This is no easy question to answer and each person must find their own understanding if they are to pursue this path.
For me the answer lies in the blackberry.
The blackberry is a thorny plant that grows in shrubs. Like the blackthorn it grows a white flower in spring. Like the blackthorn it also produces a dark purple-black fruit in fall. Interestingly enough, it also seems to have taboos and superstitions attached to it.
According to Robert Graves the blackberry was associated with the devil, and the fruit was either never picked –or like the blackthorn- was considered unfortunate to pick at certain times of the year. Also like the blackthorn the blackberry was considered very unlucky[xi].
The fit is not as perfect as it might initially appear, however. The blackberry rarely grows into anything resembling a tree. The native Trailing Blackberry grows along the ground while the introduced and widespread Himalayan Blackberry also mostly grows along the ground. I have seen individual branches in the forest growing straight into the air, at heights around ten feet or more, but the stems looks nothing like the trunks of trees[xii].
The blackberry is as good a substitute for the Ogham letter as I have found for my area however. What once was a mnemonic device to my ancestors became both meaningful and magical to them over time as it has for me. The important thing for me –as it should be for you as well- is to find something that honours your own path and feels right to you. As long as we remember not to sell our own discoveries as the gospel of our ancestor -and to treat the path with reverence and respect- then the Ogham path of knowledge and wisdom has much to teach us both of the past and of the possible future, as well as of the unseen realms.
Straif is not only a dark tree of power and magic, it is also mysterious and wise. In our journey through the forest it can take us places that we never imagined that we could go.
“The blackthorn’s scented white blossoms, and their contrast with its dark, spiny branches, symbolizes the general theme of light and darkness with which the plant has
been associated since ancient times. The dangerous, long spikes and the red “blood” that flows in the veins of the blackthorn tree enhance the dramatic effect even further. The blossoms, the fruits and the crimson sap display the three colours of the Great Goddess: white, black, and red. And as its name suggests, this tree has been associated with the dark aspects of life, such as night, death, and the underworld.” – Fred Hageneder (The Meaning of Trees)
[i] The White Goddess.
[ii] The Celtic Tree Oracle.
[iii] Magical Alphabets.
[iv] Ogam: Weaving Word Wisdom.
[v] The Meaning of Trees. Fred Hageneder.
[vi] Tree Wisdom: the Definitive Guidebook, Jacqueline Memory Paterson.
[vii] Oxford Dictionary of Celtic Mythology. James MacKillop.
[viii] Tree Wisdom: the Definitive Guidebook.
[ix] Oxford Dictionary of Celtic Mythology.
[x] Native Trees of Canada. Department of Forestry. 1966.
[xi] The White Goddess.
[xii] Plants of Coastal British Columbia. Pojar and MacKinnon