Read this post first: Ogham: the Forfeda, Diphthongs, or Extra Letters
“Some students find that using the forfeda enriches their experience with the ogam. Many of them would never dream of doing an ogam reading without them. Others find them problematic at best. These additional letters are not found in any of the stone inscriptions, and were added one at a time at a much later date than the original ogam letters were developed, they were certainly a part of the medieval ogam tradition and are a legitimate part of the system. The ‘Auraicept na n-Eces includes them in some of the ogam lists, but ignores them in others. It appears to me that even the medieval ogamists didn’t agree about their use.” – Eryn Rowan Laurie (Ogam: Weaving Word Wisdom)
The Roots:
Eryn Rowan Laurie, in the above quote, beautifully sums up both the allure and the confusion surrounding the Forfeda and their individual meanings. There seems to be little agreement, in fact, on what any of these letters represents to anyone.
These ‘extra letters’ are also sometimes referred to as diphthongs but more readily as Forfeda. Regardless of their name, they do present us with some problematic considerations.
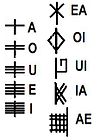
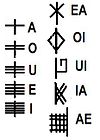
The confusion begins with the number of letters to be included. Most lists contain five but some contain up to thirteen. These longer lists are rarer. We will be focusing here on the five forfeda that are presented most commonly by various experts.
The meanings and associations for these letters also varies widely, as do their names and letter associations[i].
The first letter Ea can also be found as Ch. It is generally referred to as Aspen or the Grove[ii] (Murray) but can also be woodbine or elecampane.
The second letter Oi can also be found as Th. It is usually listed as the Spindle Tree. Other occurrences are Ivy, Heather, Gooseberry or thorn trees.
The third letter Ui can also be found as Pe. This letter can even be drawn quite differently from time to time depending on the source. It can look like a frontwards or backwards P, a hook, or an outward single swirl. This letter is usually associated with the Honeysuckle. The other occurrences are the Beech tree (Murray), or the Woodbine and Ivy (John Mathews[iii]).
The fourth letter Io can also be found as Ph. This letter is usually the Gooseberry or the Pine. It can also be found as the Honeysuckle (Murray), the thorn, the guelder rose (Pennick) or the snowball (Pennick[iv]).
The fifth letter Ae can also be found as Xi. It is generally listed as the Witch Hazel or Mor, the Sea (Murray). It can also occur as the Beech or Pine tree. In the Scholar’s Primer it’s called “the twin of Hazel” which is where the association of Witch Hazel or Beech comes from as people try to interpret what this phrase meant.
Confused yet? Aren’t you glad there’s an introduction to the Forfeda, as opposed to us just jumping in with both feet?
The Trunk:
The Ogham Tract, or Scholar’s Primer, is the most common source used to determine the meaning of the Forfeda by reconstructionists[v]. As far as an Ogham divination or magical source the most common used list is the one that was proposed by Liz and Colin Murray in the Celtic Tree Oracle. This is the reason that I placed in brackets the expert’s names above who stood out independently from all the others. For the most part I follow the Murray’s listing despite their misplacement of Honeysuckle and Beech. ‘The Grove’ was their solution to the recurrence of Aspen[vi]. ‘The Sea’ replaced the confusing twin of hazel (maybe they were thinking of the Hazel beneath the sea that fed the Salmon?[vii]) or the Pine (this to me would be a repeat similar to the Aspen. Silver Fir was a mistaken identity and was actually the Scots Pine[viii]).
Before I confuse you any further, let me address the elephant in the blog post if you will. If you’ve been following the Ogham listing through this blog, or are aware of the Ogham at all, you’re probably wondering where the hell Robert Graves is on the matter of the Forfeda?
The White Goddess brought the Ogham out of the museums and universities, and handed it back to the bards and the mystics – where it also belonged. In the White Goddess, however, Graves barely even mentions the Forfeda and doesn’t contribute anything of significance to their meanings in a poetic sense whatsoever. A lesser known book titled the Crane Bag and Other Disputed Subjects, on the other hand, contained an essay by Graves on the Forfeda. The following passages quote portions of that essay.
“I can best make my point by quoting [Dr. Anne Ross’] three-page treatment of an important Celtic myth that of the Sea- God’s Crane Bag; and her general view of cranes in Celtic tradition. The Crane Bag, she informs us correctly, belonged in Irish legend to Manannan God of the Sea and had been made from the skin of Aoife (‘pleasing’), a woman magically transformed into a crane. In this context Dr. Ross quotes an early medieval Irish Text[ix] which she calls ‘full of interest from a mythological point of view’. It certainly startled me:
“‘This crane-bag held every precious thing that Manannan possessed. The shirt of Manannan himself and his knife, and the shoulder strap of Goibne, the fierce smith, together with his smith’s hook; and the king of Scotland’s shears; and the king of Lochlainn’s helmet; and the bones of Asil’s (Assail’s) swine. A strip of the great whale’s back was also in that shapely crane-bag. When the sea was full, all the treasures were visible in it; when the fierce sea ebbed, the crane bag was empty.’”
Robert Graves then spends some time trying to solidify his Greek alphabet-Ogham connection that he had already dealt forth in the White Goddess. He then lists the numerous reasons why the crane was sacred to both the Celts and the Greeks. This is followed by references from Macalister’s Secret languages of Ireland and Calder’s The Scholar’s Primer. Graves tries to assure us that the poets used the Ogham as a secret code.

“That the crane bag was filled when the sea was in flood,” Graves continues, “but emptied when it ebbed, means that these Ogham signs made complete sense for poetic Sons of Manannan, but none for the uninitiated outsiders. The Crane Bag, in fact, was not a tangible object, but, like Athene’s Goatskin Bag, the Aegis, which contained the Gorgon’s head, existed only as a metaphor, No more than two of the regular twenty letters which it contained are described in pictographic form by the poets quoted by Dr. Ross; namely M and G, the initials of Manannan and Goibne the Smith. These consist respectively, of one, and two nicks of the diagonal letter group crossing the stem-line. They are here disguised in ridding pictorial terms as ‘Manannan’s Knife’ (stuck in his belt) and ‘Goibne’s shoulder strap’ (which crossed his belt to his sword) and are offered merely as samples of the more ancient letters. As for the other miscellaneous objects found in the Crane Bag: if one thinks poetically, not scientifically, their meaning leaps to the eye.”
These items are listed as ‘the King of Scotland’s Shears’(the X), ‘the king of Lochlainn’s helmet’ (with his face underneath, the four sided diamond), ‘the bones of Assail’s swine’ (the double lined X out to the side of the line), ‘Goibne’s smith-hook’ (the P or hook symbol), and Manannan’s own shirt’, which “is a map of the sea showing lines of longitude and latitude.”
Graves then starts to ponder over the meanings of these treasures. He thinks that the first letter, CH, may have been the beginning of the name of a Scottish King (as a mnemonic device used in much the same way that each tree was chosen to represent a certain letter) and that perhaps the King of Lochlainn (Norway or Norse settlement of Dublin) could have had a Th letter name, like Thor.
Graves then surmises that the bones of Assail’s swine are possibly the crossed stalks of sacred mushrooms (Mushrooms are ‘little pigs’ in Latin and Italian) that had been discarded, “as bones from meat.” Graves has already explained Manannan’s shirt and he does not emphasize any further on Goibne’s fish hook.
“But I hear some conscientious reader complaining, ‘Hi, wait a bit! What about the strip of whale’s back in the Crane Bag?’ That was so easy that I left the explanation out. Ogham nicks make no certain sense without a stem line; and for a Sea-God the only possible stem line was the horizon-dark and slightly arched like the back of a whale.”
Robert Graves then puffs out his chest a bit, pats himself on the back enthusiastically, and then exits off stage to the left… thus concluding his essay.
Colin Murray, in the Celtic Tree Oracle, made it no secret that he was using both the Ogham Tract (Book of Ballymote) and the Crane Bag and Other Disputed Subjects as the two sources for his and Liz’s listings of the Forfeda found in their book.
“The knowledge of the Crane Bag as displayed in the interpretation by Robert Graves is a fine example of the poetic insight needed to relive the perception of the old poets and Bards and to understand their way of thinking.”
The book’s introduction then shares a Scottish folk poem from Alexander Carmichael’s Carmina Gadelica. In the poem, a monster is captured and forced to build a house before he will be released. This monster sings a song as he’s working, which basically says that he’s including every tree of the forest except for the wild fig and Aspen, and in a later version of the same song the Yew, the Blackthorn and the Ivy are the trees that are removed from the dwelling. According to Murray, by leaving out these trees the monster has essentially cursed the home owner from ever being reborn to a better life, as well as, “the determination and self knowledge that would be necessary for it to succeed.” Of course, again, the hidden aspects of the tale are only present for someone who has knowledge of the Ogham or the tree meanings in Celtic tree-lore. Liz and Colin Murray end part one of their introductions as follows:
“This brief introduction to the trees in the forest of Celtic knowledge should have provided an insight into the way the tree knowledge was described, revealing itself only to those with the appropriate understanding. This leads us on to actually using Ogham and its hidden meanings in the search for the inner man and woman.”
In the Ogham Tract it’s clear that the medieval experts didn’t agree on a meaning or listing for each tree found in the final set of letters. Robert Graves, on the other hand, did not suggest – even once – that the last five “extra” letters were trees at all.
Robert Graves, by defining more clearly the shirt of Manannan, left us with Mor, the sea, as the final letter of the Forfeda. At least that’s the most likely place from which Colin Murray took the meaning of “the Sea” from.
I believe that Colin Murray, using the King of Lochlainn’s shears as a clue, decided that the first letter of the Forfeda was the Grove. In a mythological or symbolic sense, if the undergrowth of the forest were to be cut down, as a sheep would be sheared, the action could in fact create a Grove.
I also believe – and this is only a theory that cannot be verified – that Colin Murray was working on discovering the metaphorical meanings of the last few letters of the Forfeda. These were listed in The Celtic Tree Oracle as the Spindle, the Honeysuckle, and the Beech tree. Is it possible that Colin passed away before he could discover them? Perhaps he already had, and these were left in his notes unrecognized for what they really were, hidden in plain sight before the Celtic tree Oracle was ever published?
Also to be considered, John Mathews in the Celtic Shaman explores the possibilities of deeper meaning to all of the letters in the “riddling glosses” found in the Word-Oghams. He also presents clues associated with Finn or Fionn’s wheel, the Celtic Mandela diagram.
The Foliage:
The Forfeda offers us an opportunity for the student of Ogham. It seems clear, to me anyways, that these letters were added at a time when the Ogham had already become a magical alphabet, and when the Ogham was no longer just being used as a land marking device. The difficult nature of the Forfeda does give the Ogham student the opportunity to explore these “extra letters” and come to their own conclusions, however. These next five letters will be presented in a way that speaks to me. This is in no way the final say on anything. In fact, this section will be far more Neopagan than reconstructionist.
In the Celtic Tree Oracle the Forfeda are included as regular divination cards. These cards are, perhaps, similar to the major arcana of the tarot. Some systems use the Forfeda on a casting cloth upon the ground. The twenty letters are then thrown upon these “extra” five letters in an attempt at divination, as well.
Mythological and magically, these final letters seem to be missing their place within the myths and legends of the Celtic ancestors. This is why the Manannan Crane Bag legend fit so nicely into my own system of study and meditation. It’s clear from the differences of opinion found in the Book of Ballymote – especially within the Ogham tract – that the truth of these letters may never be fully known. There’s a fine line to walk here then.
It’s important to remember, that this attempt at reconstruction may be nothing more than fallacy. This is especially true when one considers the historical sources and the contradictions that we’re left to work with.
There’s one final thing to consider, as well. In the Celtic Tree Oracle Liz and Colin Murray speak of Dr. Berry Fell’s discovery of Ogham carvings in America and Brenda Sullivan’s similar theories about rock carvings found in Africa in the appendix. These ideas have been thrown aside by scholars for a wide variety of reasons including time frame impossibilities and there being greater differences than similarities in the lettering[x]. Many of Robert Graves’ theories have been disproven and have not stood the test of time either. Though he came from a place of poetic inspiration he also riddled his writing with factual inaccuracies that are too many to name[xi].
I’ve always enjoyed the work of Joseph Campbell. In reading the Hero of a Thousand Faces or watching his famous interviews on the Power of Myth – taped on the Skywalker ranch – I’m reminded just how similar we can sometimes evolve as people, mythological and completely independent from one another. Dragons and little people exist within cultural beliefs found almost everywhere. So do ghosts and the undead. There are Cinderella motifs and the hero’s journey found all over the world. The shaman, and the otherworld in which he travels, is found throughout every region of our planet, as well.
It’s my personal belief, that these mystical encounters either spiritually, evolutionary or psychologically, are part of our human experience. I do not believe that because a shaman from Africa goes to a similar place (Otherworld) as a shaman from Hawaii or El Salvador that this must be because there was physical over-land or sea travel which brought the exchanging of ideas thousands of years ago. These lines many of the researchers of the past make in the sand, for similar arguments, are shaky at best. Perhaps similarities of belief are more innate than science can realize in its present infancy?
I believe that without Robert Graves the Ogham would currently be nothing more than a footnote in a legend, or a tourist attraction at the corner of a churchyard or on the back of some farmer’s field. I do not believe as he did, however, that our ancestors needed to carry the religious practices of the Greeks or Hebrews all the way to Ireland to create a new, previously nonexistent, magical system of beliefs. They already had their own[xii].
Whatever it is that I believe or look into, though, I must always be open to the possibility that my opinion may change due to new discoveries or to things that I’d previously overlooked. I feel that as we start to explore the Forfeda that this statement is an especially important one to make.
The opinions that follow, on the Forfeda, are not as fixed in my mind as most of the other letters of the Ogham.
“There is a forth function of myth, and this is the one that I think everyone must try today to relate to – and that is the pedagogical function, of how to live a human lifetime under any circumstances. Myth can teach you that.” – Joseph Campbell (The Power of Myth, 1985)

[i] Robert Graves was a poet not a historian. Many new Ogham users make the mistake of seeing him as an academic, and assume his work is historically accurate.
[ii] Occurring in the forest, but not a tree itself.
[iii] The Celtic Shaman.
[iv] Magical Alphabets.
[v] http://www.maryjones.us/ctexts/ogham.html
[vi] A partial reason?
[vii] Another partial reason? Read on to learn about the shirt of Manannan.
[viii] See the Ailm blog entry. Scots Fir was the name used for Scots Pine at the time that the Ogham Tract was written. The Silver Fir had not been introduced into Ireland at the time this tract was written. Like other variations of names in the tract (furz/gorse or Sloe/Blackthorn) the Pine and the Fir tree which were listed are actually the same tree. The variation in name is likely poetic flair, but may also have been a translation error.
[ix] MacNeill, 1904, VII, 21 (Robert Graves footnote)
[xii] We shouldn’t overlook the fact that it was most often Christian monks who wrote down the first Irish legends. Forever grateful we should be, they could not have helped but to have seen the Celtic world through their own religious paradigms, though. This would have coloured the old stories in many ways.